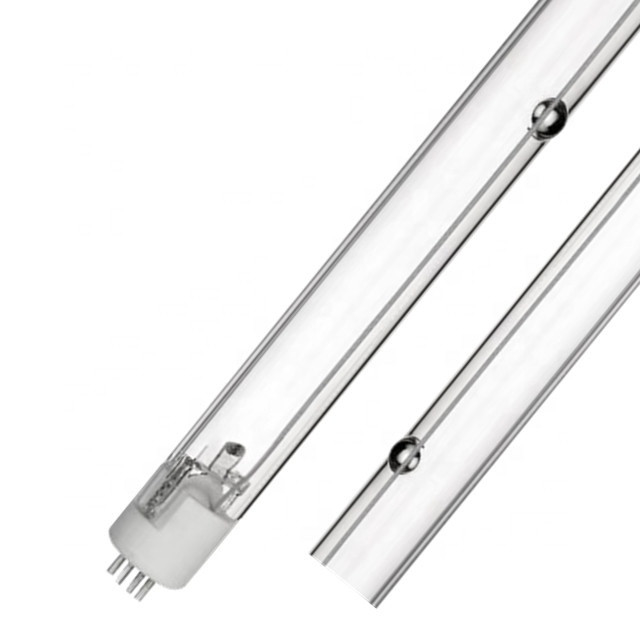
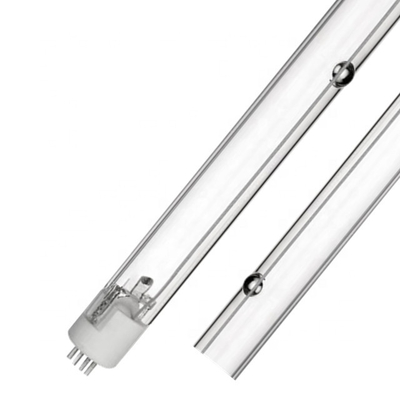
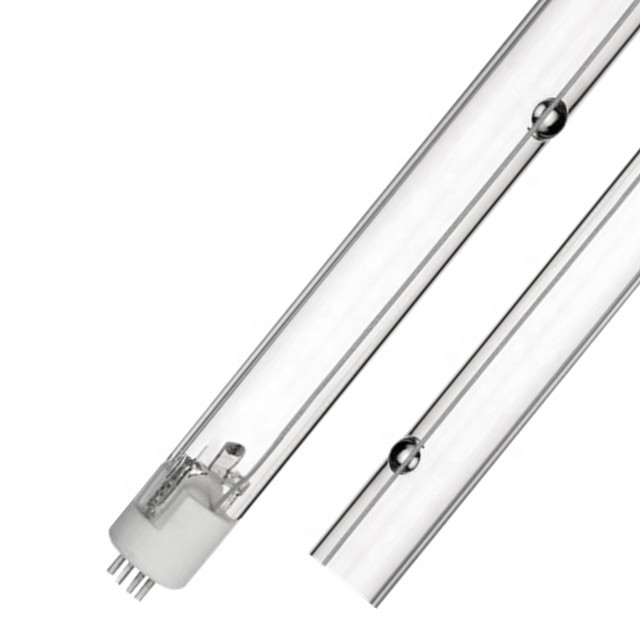
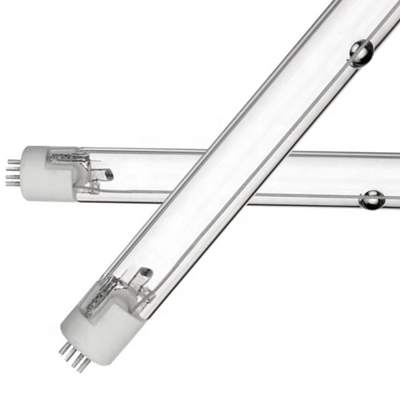
Microorganisms are simple organic structures that can easily absorb UV-C wavelengths, causing
photodissociation (destruction). Microbial DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is first adversely affected due to its weaker molecular
bonds. Within a hundredth of a second, it suffered irreparable damage. The subsequent loss of genetic instructions can cause the
cell to die and/or fail to replicate, making it harmless. Continuous exposure will cause uninterrupted degradation, such as the
sun, which will only be significantly faster.

Leave a Message
We will call you back soon!
 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
 Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!
SUBMIT
More information facilitates better communication.
Mr
- Mr
- Mrs
OK
Submitted successfully!
We will call you back soon!
OK
Leave a Message
We will call you back soon!
 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
 Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!
SUBMIT







